There are multiple ways to gain links from the internet through both direct and indirect efforts. Direct methods include activities like sharing documents, guest posting, and distributing press releases via social media.
Indirect methods involve creating appealing content on your website, encouraging visitors to share it widely, which naturally forms links across various sites.
The value transferred through these links is termed ‘link juice,’ which varies depending on the linking sites’ authority. Understanding link juice and its impact on your site’s authority can significantly enhance your search engine optimization strategy.
What exactly is link juice, and how does it contribute to a site’s domain authority? Let’s explore.
[toc]
What is link juice?
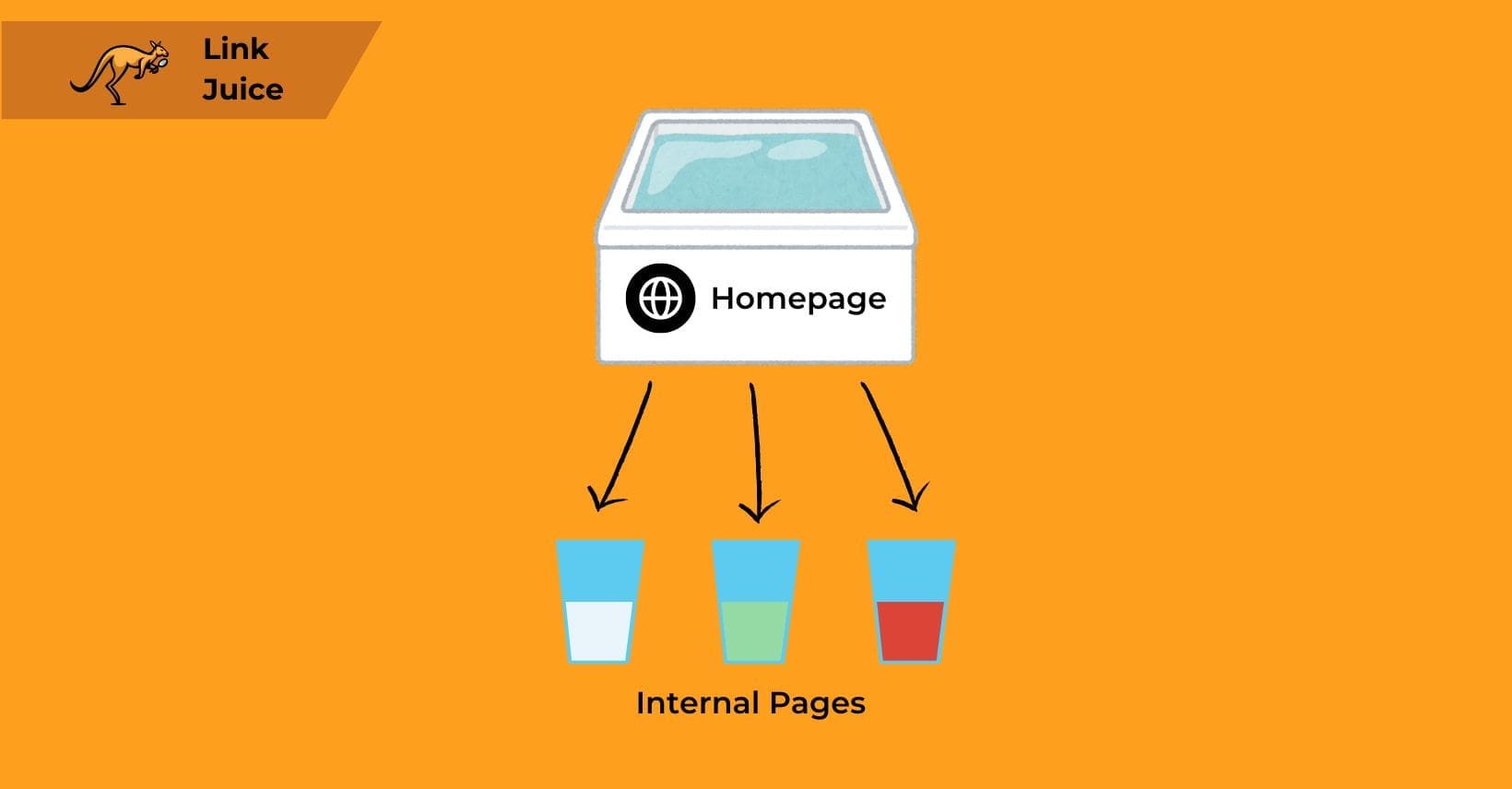
“Link juice” refers to the power a backlink transfers to another site to help improve its position in search results.
Known also as “link equity,” this concept is vital in SEO as it represents the authority or value a backlink carries. Websites with high authority that link to other sites provide more link juice, boosting the recipient’s visibility on search engines like Google.
The ability of a website to rank for specific keywords largely hinges on the accumulation of link juice from robust, authoritative sources.
Although Google has discontinued its PageRank tool, the idea of evaluating a site’s value based on backlinks persists in practice, shaping how well pages perform in search rankings.
As we consider the influence of these connections, it becomes clear that understanding the mechanics behind link juice can illuminate why some pages rise in search results while others do not.
How Does Link Juice Work?
Link juice enhances a page’s visibility in search engine results.
While it isn’t the sole factor in ranking, it ranks highly as a key influencer. By employing internal links, the link juice that reaches one page can be distributed throughout your website, often boosting rankings.
For instance, consider two websites, A and B. If site A has a page linking to it and site B does not, under similar ranking conditions, site A will likely outperform B due to the additional link juice from that external link.
The effect of link juice can vary; if site B gains a linking page, the outcome will depend on how much link juice each link transmits.
It’s also vital to note that link juice can flow in multiple directions, which impacts how much each site receives. Previously, nofollow links could control this flow to prevent link juice from moving away through outbound links, a strategy known as PageRank sculpting.
However, nofollow links now count towards link connections, meaning link juice can still escape, even if nofollow attributes are used on outbound links.
Understanding the mechanics behind this flow, such as the volume and quality of link juice each link imparts, leads us to consider how exactly link juice is calculated
How is link juice calculated?
Understanding link authority flow, often referred to as link juice, through do-follow links is essential.
This concept represents how authority passes from one web page to another, though it’s difficult to measure accurately due to Google’s secretive methods regarding its algorithm and link analysis.
However, there are key factors that SEOs and SEO tools consider when calculating how much value a link passes on to the page to which it links. Some of these include:
The website authority of the page the link is from
When a link originates from a reputable website that has been around for a long time and boasts a collection of high-quality content, it tends to carry more weight than a link from a website with lesser authority.
The web page’s protocol also influences this valuation; for instance, pages marked with HTTPS are considered more reliable than those with just an HTTP prefix.
This highlights the basic principle that the trustworthiness and security features of a website contribute significantly to the quality of its links
The basic type of link
The “no-follow” property tells crawlers not to follow a link. While some recognize the value of no-follow links, it is actually the do-follow links that transfer authority between pages.
Understanding how these links affect page ranking could lead to a deeper discussion of the importance of link-building strategies in SEO.
The content of the page
The value of a backlink depends on factors like content relevance, the number of links on a page, and the link’s placement.
For instance, a link in the main body of a webpage usually provides more value than one at the bottom. Authoritative and reliable content often carries more weight than content on a free, user-generated site.
To optimize the effectiveness of your links and boost their impact, you might consider the strategies to increase link juice, starting with a few key techniques.
How to get more link juice
 External links, or backlinks, enrich your website with valuable link juice. To increase these links, consider these strategies:
External links, or backlinks, enrich your website with valuable link juice. To increase these links, consider these strategies:
- produce authoritative content to establish your site as a primary source of information on particular topics
- position your website as a helpful resource, and write guest blog posts for other sites in your industry
- joining relevant industry groups,
- securing mentions through public relations efforts, and
- repairing broken links with link reclamation methods
Are effective ways to gain more backlinks. Enhancing the connectivity of your site not only strengthens its current web presence but also prepares it for more internal linking, fostering a more interconnected content structure.
Internal Linking
Your website, often underestimated, holds valuable link potential. Marketers, while pursuing external high-value backlinks, tend to overlook the abundant link resources available on their most frequented pages.
By tapping into these, you could significantly boost the authority of your internal pages with just a few site-wide links.
Initiating internal linking strategies begins with keyword identification, for which numerous free tools are available to assist you.
After selecting your desired keywords, pinpoint pages on your website that feature these terms. Employ intext search techniques to determine which pages possess the highest value for distributing link equity.
You can use the following tools:
- SEO Review Tools: This is a powerful tool that determines a URL’s domain and page authority. It will also tell you how many external links point to your page. To find the URL, anchor text, and authority information for your external links, use the Link Checker tool. They also provide a bulk authority checker that allows you to search ten pages at once.
- Small SEO Tools: This is a free tool that ranks supplied URLs’ domain and page authority out of 100.
- SEOmoz’s Open Site Explorer: This is another free tool. Moz’s Domain Authority, Page Authority, and inbound links may all be obtained for your page.
Once your target keywords and high-value pages are identified, link these using your keywords as anchor texts to relevant internal pages.
Be mindful to vary your anchor texts with synonyms or related terms to avoid appearing manipulative to search engines.
Additionally, consider removing any superfluous outbound links from your site. The rel=”nofollow” attribute can prevent these links from diluting your internal link equity.
You can track the effectiveness of your internal linking strategy and monitor the proliferation of internal links on a page via Google Search Console under the “Search Traffic” section.
As you refine these strategies, you may discover other resources to guide further improvements and updates.
External links
Link building plays a crucial role in SEO. External links are vital for search engine rankings because each link is a vote of confidence, signaling that your content is valuable. This influences how search engines rank your pages in search results.
Building backlinks might seem challenging since you can’t directly control who links to your site. Nevertheless, certain strategies can improve your chances of gaining these valuable links through effective outreach.
As you focus on expanding your site’s appeal through these external links, another strategic approach to enhance your site’s visibility across different regions involves using hreflang tags for international audiences. This method ensures that users worldwide find the most relevant version of your content.
Using hreflang for international websites
Websites targeting audiences in different countries often adapt their content through localization or translation, making it accessible to a wider range of visitors.
The hreflang tag is crucial here as it guides search engines to various page versions, helping them serve the most appropriate version based on the viewer’s language or location.
By linking pages with their localized counterparts through hreflang tags, it not only boosts their potential to rank in local search engines but also facilitates the flow of link equity between them.
Adding hreflang tags to your XML Sitemap simplifies the task for search engines by pointing them towards all your pages, including their translated or localized versions, in a unified document.
As we polish our website’s global appeal and ensure that each visitor finds content in their language, it’s also important to consider another strategy that keeps our digital presence robust: link reclamation.
Link reclamation
Link reclamation involves fixing or updating broken links to your website. Start using a tool like Site Crawl or the Google Search Console to identify URLs showing a 404 error.
Tools such as Ahrefs can then help trace back to sites that link to these broken URLs. Once found, you can contact the site owner to replace the broken link with a current one, ensuring the replacement link is directly relevant and not just redirecting to your homepage.
Incorrect redirects, especially to the homepage, may lead Google to misinterpret it as a non-functional page, reducing your site’s effectiveness in converting visitors.
Despite the clear risks, many websites still frequently encounter this problem
Leveraging Searcharoo for Enhanced Link Juice Optimization
At Searcharoo, we maximize your website’s SEO potential by optimizing link juice. Our platform provides tools to evaluate your backlink profile, pinpointing beneficial and detecting harmful links.
We also help you find new linking opportunities by connecting you with high authority domains for potential collaborations. Our automated features simplify building links and enhancing internal connections, keeping you ahead.
Our support for hreflang tags benefits international websites by optimizing link distribution across different regional versions. You’ll have access to detailed metrics and reports showing your SEO efforts’ direct effects.
Moreover, we offer educational materials like tutorials and webinars to assist you in understanding link juice optimization.
We also boast a supportive community and responsive customer service to answer your SEO queries or share insights in our forums. Committed to boosting your site’s SEO through efficient link juice management, Searcharoo is here to help you succeed.
Final Thoughts on Maximizing Link Juice
Link equity is an important part of link building, and the link juice passed to your site by external links pointing to your web pages is vital to the visibility of your site on Google or other search engines.
Because all links pointing to your site pass link equity, to get more link equity, all you need to do is obtain more links to your site.
Paid links are one option for this, but what you really need to be doing is ensuring that your page’s content is valuable enough for website owners to organically link to your quality content and its linked keywords. For a curated list of Web 2.0 sites, click for info to access valuable resources for expanding your online presence.
A high number of links is important, but those links have to be good links. A good backlink passes a large amount of link juice to your site, which you can then redistribute around your other pages using internal links.
All of this helps Google to see your site as having a high level of authority and topical relevance, which helps more traffic to find pages on your site. Link juice is not the only thing you need to consider, but it is an important factor and one you can’t ignore!


