The Google algorithm remains largely secretive, with Google intentionally keeping the specifics of its ranking system private to prevent manipulation, though key elements include content quality, backlink profiles, user experience metrics, and technical performance factors that collectively determine search visibility.
SEO factors impact Google rankings by directly influencing how the search engine evaluates and positions websites, with properly implemented SEO techniques enhancing content visibility, improving user experience metrics, and building site authority that leads to higher positions in search results. Despite the prevalence of misinformation and the continuous evolution of Google’s algorithm, certain practices that were effective in 2010 may no longer yield the same results today.
The essential factors to understand about Google’s ranking algorithm include its focus on user experience, content quality, technical performance, and authority signals, which must be integrated into a comprehensive SEO strategy that prioritizes delivering genuine value to users rather than attempting to manipulate search results.
Here, we will provide a detailed examination of the known Google ranking factors that impact search results. It’s important to stay adaptable; as Google’s algorithm evolves, so should your SEO approach.
As we dissect these factors, you might wonder exactly how they fit into the broader schema of Google’s criteria for ranking pages. Let’s explore this further.
What is a Google Ranking Factor?
Google ranking factors are specific elements that influence where your website appears in search results, determining visibility and position based on Google’s complex algorithm that evaluates quality, relevance, and user experience.
Google utilizes hundreds of ranking factors in its algorithm, with some factors carrying significantly more weight than others, which collectively determine how websites are evaluated and positioned in search results. When users search for terms related to your site, these factors determine the timing and placement of your website in the search results.
The primary focus of Google’s ranking factors is on delivering quality, relevance, and value through content that addresses the searcher’s queries.
Given their impact, you might wonder which specific factors Google prioritizes and how they affect the visibility of most websites.
As we examine these pivotal components, we’ll also hint at understanding the top Google ranking factors that shape search experiences.
Top Google Ranking Factors
The critical ranking factors for websites in Google search include content relevance, backlink quality, page loading speed, mobile optimization, and user engagement metrics, which collectively determine whether your website appears on the first page or is buried deep in search results.
The specific ranking criteria Google uses for SEO assessment include content quality, backlink profiles, page loading speed, mobile responsiveness, keyword relevance, and user engagement metrics, which collectively determine how effectively a website meets both user needs and Google’s quality standards. Google ranking factors differ for websites versus blog posts because websites are evaluated on overall domain authority and site structure, while blog posts are judged more heavily on content freshness, keyword relevance, and engagement metrics, meaning each page type requires specific optimization approaches to perform well in search results.
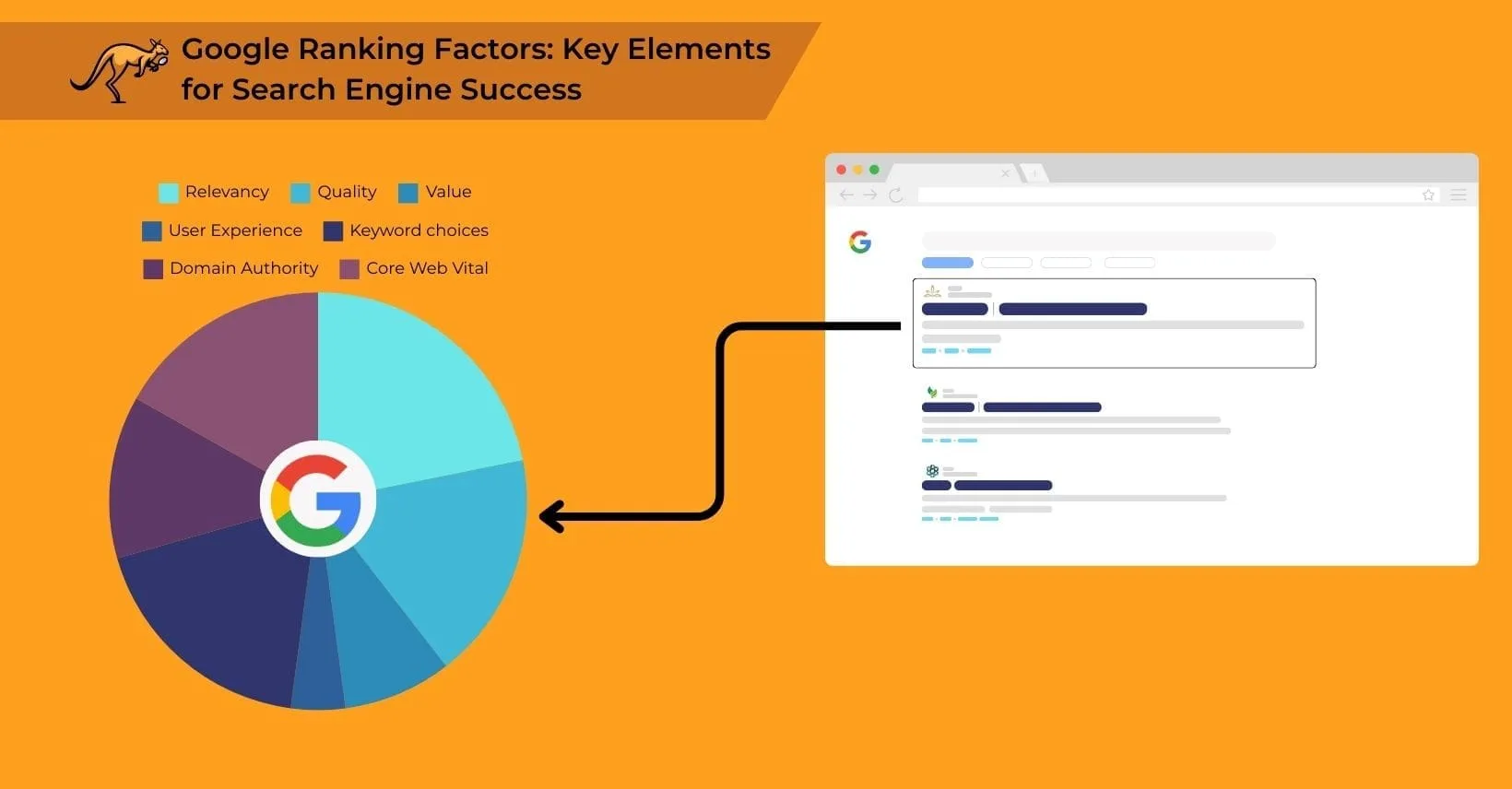
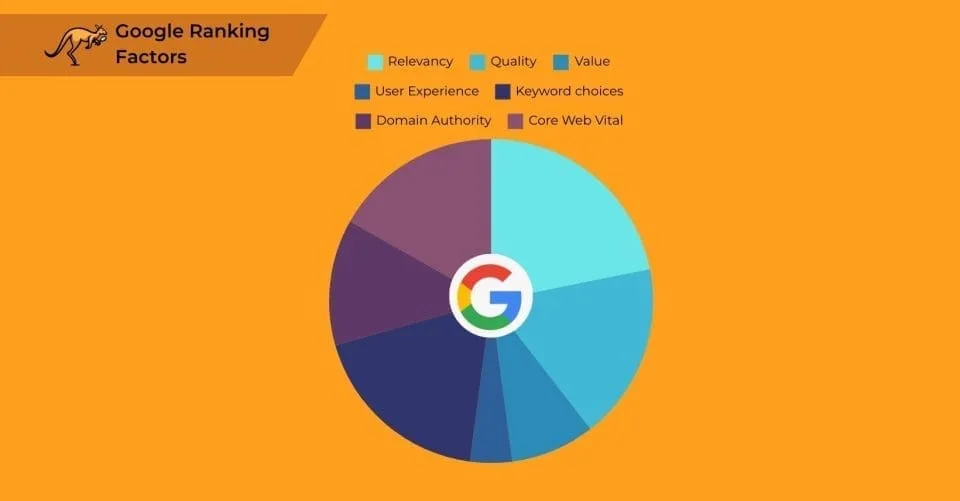
The most important Google ranking factors that form the core components of search engine rankings include Relevancy, Quality, Value, User Experience, Keyword Choices, Domain Authority, and Core Web Vitals, which together determine how Google evaluates and positions websites in search results.
Relevancy
Relevant content is the king of search engine results.
If your site does not have anything to do with the search that a user is making, then you simply are not going to appear, no matter how hard you try to force it with underhanded SEO tactics.
While this might sound obvious, it is important to remember that relevancy can be a spectrum.
If your page is in the right niche but does not match the user’s search intent, then Google is less likely to show it because it is not actually answering their question or meeting their needs.
Relevancy is not always considered a “true” ranking factor because it is simply part of how search engines work, but it forms the basis of all search results.
Your site generally will not appear for a user unless they are searching for you, your products, or a query that your site is able to answer.
Quality
Quality content makes a massive difference, too.
While it can take a while to understand what high-quality content actually is at first, it generally just refers to any page that is well-constructed and offers some actual value.
You basically want to create content that is original, helpful, and has proper value behind it (see below for more details on that).
Your content needs to be a good part of the user experience, so it should also be properly readable and actually provide the reader with the information that they need. Quality leads are essential for effective marketing strategies, ensuring that your content resonates with your target audience and drives meaningful engagement.
Take tutorial articles as an example.
The best high-quality tutorials guide the user through what they need to know while being helpful, well-structured, and written with either professional experience or proper research behind them.
Value
Value is essentially a mix of the above two factors.
If your site can provide something of actual value to the user, such as an answer to their questions or a set of products that fit their needs, then you are far more likely to rank higher.
However, this also applies to the content itself. High-value content is not just relevant but actually helpful, providing something important.
This might mean information that is not available elsewhere online or infographics and tutorials that explain something to a less-informed user.
In other words, high-value content is anything that is useful, interesting, or a combination of both – specifically in the context of your target audience.
For SEO, all that really matters is that your intended audience finds the content incredibly valuable.
Having more value behind your content than the competition also helps.
If you make sure that you are offering a more complete user experience or answer than your competitors, then you will often find that page slowly bumping higher up the search results.
User Experience
The user experience is another vital part of your Google ranking factors.
Google has ways of telling when web pages are poorly designed or if they do not retain users for longer than a single short visit, and sites that fail to actually function properly are often penalized.
However, this does not always mean that your site is fine just because it loads properly. You want to create a site (and page) that offers a good on-page experience to anybody who is using it.
If your overall user experience is bad, then users are going to stop engaging with the site – and Google will notice.
Whether it is streamlining the design of the page or updating the content to a more modern format, you want to create a site that is comfortable to use.
More importantly, you want to make sure that users can actually find what they are looking for, especially if you are using SEO to attract potential customers.
A badly designed website (whether it is on the technical side, the visual side, or both) can massively harm your SEO. Google’s ranking algorithm prefers websites that are usable, functional, and offer plenty of value to users. Therefore, investing in a reliable blogger outreach service can help improve your site’s usability and boost its search engine rankings.
Keyword Choices
Keywords are a massive part of SEO, and doing proper keyword research is essential to knowing which terms you should even be trying to rank for in the first place.
Keywords also help you better understand the audiences you are meant to be targeting.
Relevance is a massive part of how Google operates, and most relevance is judged with keywords. If a user makes a search query, Google is looking for terms similar to the ones that they have searched for.
This means that your page is more likely to appear if it uses similar or identical terms, focuses on a highly related topic, and is just generally related to what they were searching for.
Doing basic keyword research presents you with keywords relevant to your site and audience, letting you see what kind of words and phrases are most likely to be used by your potential customers.
These are the terms you want to rank for in most cases.
Good keyword research can provide you with a long list of potential keywords to target, as well as their search volume.
Of course, keyword research also shows you the most competitive keywords out there, the ones that are dominated by larger companies that are very difficult to overtake.
Keywords are basically an entirely separate topic that can get incredibly complex and in-depth.
In general, you want to rank for keywords that are relevant to your site and your audience, not so competitive that they are impossible to achieve, and varied enough to capture your entire audience where possible.
Domain Authority
Domain authority is basically the amount of trust that search engines have in a site.
Higher domain authority means higher positions in search results, but it also means that any outbound links those sites place to another website are also far more valuable.
Ranked on a score from 1 to 100, DA basically tells you how likely you are to rank on Google for topics related to your own brand, services, products, or expertise.
This also has a particularly strong effect on links (see the backlinks section further below), changing how much SEO potential links from a site will have on others.
While DA is not a measurement that Google itself uses, it is still important for getting a quick measurement of your performance and the chances of being a top-ranking site in that specific niche.
Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals, a set of recent Google ranking factors, assesses a site’s health based on user experience metrics.
These include three key components: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
LCP measures the time a page’s main content takes to load, with a target time of under 2.5 seconds to avoid user drop-off.
FID evaluates a page’s responsiveness, aiming for an interaction time of 100ms or less to prevent user frustration due to delays caused by excessive code or poor design.
CLS focuses on visual stability, ensuring the page does not shift unexpectedly during load, which can disrupt the user experience.
These factors influence user satisfaction and impact a site’s ability to rank well in search results. With this understanding of website performance metrics, one might consider how these interact with other content-related Google ranking factors.
Content Google Ranking Factors
High-quality and valuable content is key, but let’s zero in on what truly elevates rankings.
Content plays a pivotal role in website rankings and often emerges as the top factor influencing a page’s position.
Google aims to present users with the finest content matching their search intent, prioritizing not just relevance and quality but also the originality of the content and the effectiveness of its title structuring.
This leads us to consider how structures, creativity, and keeping information current play into crafting content that stands out.
Content Structures
High-quality content is not just about the words themselves but also the overall quality of the content as a readable piece of media.
Google will prioritize a piece of content that is well-formatted and easy to read over a mess of information with no clear titles or subheadings.
A proper structure can be one of the more often overlooked ranking factors.
For example, using headings and subheadings (the H2, H3, H4, etc. tags) and adding in bulleted or numbered lists can boost your SEO ranking potential.
Additions like a table of contents can also help, both because they make the user’s experience easier and keep everything streamlined.
If you have no real structure to your content, then not only will Google often lower its ranking potential, but readers will find it harder to engage with the solid wall of text you are giving them.
Originality
Original content is better from both a ranking standpoint and a link building standpoint.
If you are simply re-writing information that already exists on the internet, you are not contributing anything new – Google will not penalize you, but it also will not give you any special boosts.
It is best to create original content whenever possible.
Create webpages that respond to certain questions or articles that explain specific things, such as how-to tutorials for a very niche product.
Information like this is often less widespread, so you are going to get more of a presence on search engines.
Beyond that, duplicate content is a no-go. Never copy something wholesale from another site or even from your own if you can help it.
Google will penalize duplicate content, and that means reductions in your Google rankings or other potential problems going forward.
Freshness and Up-To-Date Information
Users search on Google typically seek the most current information available.
Google and other search engines recognize this demand and prioritize fresh, relevant content. This is true for a variety of content, from breaking news and medical articles to DIY guides.
Updating older content is crucial for the same reasons: satisfying Google’s ranking algorithms and delivering the needed information to users.
Outdated content can result in users quickly leaving the page, negatively affecting Google’s assessment of the site’s quality.
Furthermore, certain topics may only temporarily surge in popularity. For instance, releasing a new celebrity album might temporarily boost search volumes, but interest wanes over time.
Maintaining relevancy in content caters to immediate user interests. It subtly influences other SEO aspects, such as how external links contribute to site credibility and rankings.
Link Ranking Factors
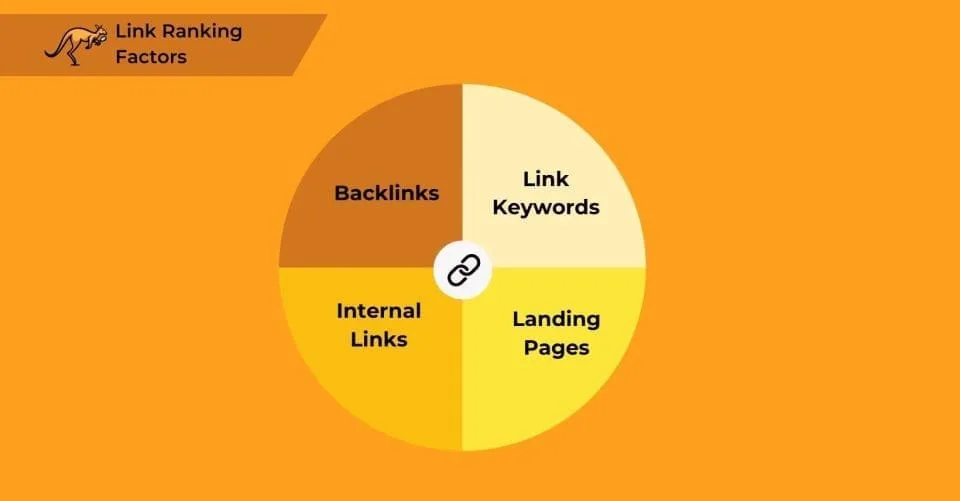
Links are crucial to SEO effectiveness. Nearly 90% of websites lack a substantial backlink profile, attract few visitors, and are buried beneath pages with even marginally better rankings.
Conversely, sites with poorly organized internal links can become difficult to navigate, reducing usability. Google’s crawlers rely on links to navigate websites, and most SEO strategies focus on links’ ability to transfer domain authority from one site to another.
This transfer is pivotal for enhancing your site’s visibility and ranking in search results.
As we consider the impact of links on a site’s performance, we’ll look into the elements that contribute to effective link-building strategies, including the types of links, like backlinks and internal links, and how they can influence the authority and usability of a landing page.
Backlinks
A site with no backlinks gets no visitors.
Google takes backlinks into account for any rankings, and they are one of the top Google ranking factors for a reason.
In general, backlinks are any links that point back at your site from another one, transferring some domain authority (also known as “link juice”) with them.
Backlinks are an entirely distinct SEO element that could take multiple articles to explain in depth.
In simple terms, if a high-quality and trusted website links back to your own, you gain a little boost to your rankings due to the trust that is being transferred from that site to yours.
This means that having a lot of high-quality links directed at your site makes you rank much higher in search results for relevant topics.
Sites (and individual web pages) that have a good link profile behind them are incredibly valuable and usually rank very high compared to other pages.
However, relevance also applies here. Links from spam sites, or links from sites and content that are completely unrelated to your business, can have the opposite effect.
Google may even penalize sites that are clearly buying low-quality links or using other black-hat link building methods.
Internal Links
Internal links (pointing from one page on your site to another page on your site) are how users navigate around.
They also provide context to search engine crawlers and make sure that both users and crawler bots can actually get to the pages that you want them to reach.
Internal link anchor text (the text a link is attached to) is just as important as it is for backlinks.
You want internal site links to make sense and be relevant – if a user clicks on a link that says “About,” they do not want to go to the Contact page.
While they are less of a major Google ranking factor than backlinks, these internal links are still a huge part of your site’s technical SEO.
Link Keywords
No matter which link types you are dealing with, keywords are vital.
Just like in other forms of marketing and search optimization, keywords dictate the terms that you are actually trying to rank for, which is the core of how relevance works.
A lot of ranking factors only apply if a user searches for relevant terms.
These are your keywords. Your site can only properly rank for terms that are related to it, whether that is a business or product name to something more vague like “Furniture” or “DIY tutorial”.
In the context of links, search engines only really give value to outbound links from relevant websites, and that includes their content.
You ideally want every link pointing to your site to come from a piece of very relevant online content and be attached to a very relevant keyword.
For example, if your furniture site is linked to by a furniture blog, that is relevant and boosts your rankings in search results.
However, if the link is placed on the words “shop now,” but your target keyword would be something like “antique furniture,” you are not getting the best results.
This is another part of link building that is best explained separately, but the basics are usually quite easy to understand: links become more powerful if the origin site/page and the target site/page have similar keywords and niches.
Landing Pages
A landing page is typically the first page a user encounters upon arriving at a website, determined by the links they click or the search results they choose.
While any website page can serve as a landing page due to its discoverability through search engines, many websites designate specific pages, such as the homepage, that are intended to be the initial point of contact.
A landing page’s relevance increases when linked from another site.
The landing page’s content should directly relate to the link’s anchor text to ensure the link source and destination coherence. For instance, a link to a particular product should direct users to that product’s page, not to a general page.
This focus on relevant linking underscores the importance of well-structured web pages, allowing a deeper look into how on-page and technical elements contribute to SEO ranking factors.
On-Page and Technical SEO Ranking Factors
On-page quality is crucial for Google rankings, directly influencing user experience.
This includes more than just page speed; it encompasses the underlying code and metadata associated with each title tag and image. Although users may not see all on-page elements, search engines do, and these components significantly affect your site’s search placement.
Ignoring these elements is like overlooking critical structural aspects of your website.
Among these factors, Mobile-First Compatibility and Optimization, as well as Image Alt Text and Title Tags, play key roles in determining how effectively your content connects with search engines and users.
Mobile-First Compatibility and Optimization
Google’s mobile audience is massive, making up more than half of all searches.
This means that you need to think about mobile-first optimization and create mobile-friendly pages that can actually support mobile users properly.
Google’s mobile audience is so huge that sites are actively penalized if they do not support mobile devices properly, either through an alternative version of the site that is optimized for mobile or a responsive design that adapts to any device.
The algorithm that Google uses focuses on mobile-first indexing, which means that mobile functionality has a direct impact on your ranking performance.
Even if your site is great, not supporting mobile devices tanks your rankings, not to mention preventing more than half of users from visiting.
Mobile-first optimization requires a few core things: a responsive or mobile-friendly design, careful checks to ensure that no design elements make the mobile site unusable, and proper loading optimization.
Image Alt Text
On their own, images are not part of Google ranking factors – but on a good site, they would be.
This is because Google can’t actually tell what images are from the file alone and has no context for the image aside from the page it is actually on.
Google’s image search rankings are affected by several factors including descriptive alt text that explains what the image depicts, relevant file names, image quality, loading speed, surrounding content context, and proper image formatting, which collectively help search engines properly index and rank visual content.
Most alt text is a description of the image itself, which gives search engines more context and allows them to interpret the image properly.
This is also important for screen-readers, which have a similar problem of not being able to understand images.
This means that no alt text can be actively harmful to the user experience, especially if the page uses them heavily.
Beyond that, no alt text means that images have absolutely zero context when used as links.
For example, having a graphic of a “buy now!” button means nothing to Google because Google itself cannot read that graphic without alt text explaining what it is.
By adding alt text, you are able to help Google understand the images – which means that it can treat them as part of your ranking factors.
This also makes sure that people using screen readers or other similar tools are not being served content that they literally cannot engage with.
Title Tags
Effective content structure is crucial for search engine optimization, yet tags that define headings are often underestimated.
Title tags are essential for marking headers and providing Google with insights into your page’s content. This specificity helps ensure your page appears in the right search results, particularly for topics within a broader niche.
Title tags also shape how your page is presented in organic search results; they may differ from your actual page header but directly influence what your potential audience sees.
Thus, optimizing your title tag can significantly affect various SEO factors.
When adding title tags to your HTML, place them correctly and choose your words wisely. Titles should be concise and distinctive, incorporating a primary keyword and staying within 50 to 60 characters to optimize effectiveness.
The goal is to adequately detail your page’s content, targeting both Google’s algorithms and your intended audience. The title tag provides context and enhances the page’s appeal to visitors and efficiency for search crawlers.
As we refine these entry points, it becomes clear they’re just one piece of a larger puzzle involving other ranking factors.
Other Ranking Factors
While the complete list of factors Google uses to rank websites remains undisclosed to prevent manipulation, seasoned users of Google’s search tools have identified various significant factors.
Some of these factors offer minor advantages, whereas others, often underestimated due to their simplicity or less apparent nature, play a crucial role in rankings.
The fluidity of Google’s algorithm requires constant vigilance; strategies that enhance your site’s position one year may be ineffective the next. Adapting to these shifts might involve refining your content or rethinking your website’s structure.
As we consider the evolving dynamics of search engine optimization, the topic of website security emerges as a critical element, subtly influencing user trust and search engine visibility.
Web Site Security
Google’s search engine spiders prioritize website security, noting whether a site employs HTTPS over HTTP.
This security measure is crucial as HTTPS provides an added layer of protection. Sites that neglect this fundamental security step often suffer from reduced SEO rankings. Furthermore, browsers may alert users about the lack of security, potentially deterring them from visiting the site.
The presence of HTTPS is a straightforward ranking factor for search engines; it is essentially a check to see if a site meets this security standard. Prompt action is necessary, particularly for older websites that have not transitioned to HTTPS.
Looking ahead, understanding the tools that guide these spiders through your site, such as XML Sitemap and Robots.txt, becomes essential.
XML Sitemap and Robots.txt
Although XML Sitemap and Robots.txt play pivotal roles in site management, they are not directly ranking factors.
An XML sitemap guides search engine crawlers through your website’s structure, showing relationships between pages. This assists bots in efficiently navigating and indexing your site, ensuring broader page visibility on search engines.
The Robots.txt file directs crawlers on which areas of the site to skip, focusing their efforts on content-rich pages rather than on non-essential ones such as backend technical pages. This strategic guidance helps optimize the crawler’s budget, allowing them to spend more time on pages that enhance your site’s SEO rather than wasting resources.
By managing crawler activity with these tools, you effectively shape the indexing of your content, boosting the visibility of key pages. You can explore additional strategies to refine and enhance your online presence with a solid foundation.
Other Useful Options
Google ranking factors impact website performance in search results by determining visibility, click-through rates, and overall traffic potential, with well-optimized sites earning higher positions that generate more organic traffic, increased brand awareness, and better conversion opportunities than poorly optimized competitors.
These methods increase the likelihood that your site becomes the “go-to” destination for users aiming to resolve their queries, making your web pages more enticing as organic search results.
As we explore optimization strategies, integrating Schema Markup and Structured Data will further illustrate how to refine the presentation and accessibility of your content to search engines.
Schema Markup and Structured Data
Schema markup, similar to alt text, aids search engines in comprehending the contents and purpose of a webpage, enhancing the context provided to search engines alongside structured data.
This enrichment allows additional details displayed in search results when your site is shown. For instance, a pie recipe webpage could benefit from structured data.
Without it, the search result might show only the title and meta description. With structured data, search results could include a recipe preview or display the cooking time, enabling users to see this information without clicking through to the site.
Although schema markup does not directly affect ranking positions, it helps your site occupy more space in search results and present more information, improving user interaction.
This boost in visibility is key as it sets the stage for broader digital engagement strategies, such as enhancing your social media presence.
Social Media Presence
While social platforms are not directly factored into Google’s ranking algorithms, having a strong social media presence often correlates with increased website traffic and improved rankings.
This association may be because brands with robust social channels typically have the marketing savvy to optimize their web presence effectively. Additionally, the visibility gained from active social engagement can amplify site awareness and drive more traffic indirectly through increased search interest.
Engaging on social platforms might not boost your rankings directly, but it exposes more potential customers to your brand. This exposure often leads to more searches for your brand name, which can positively impact your search engine results.
Regularly posting high-quality content on these channels also helps attract organic traffic, further reinforcing your online visibility.
Brand visibility is crucial, so understanding how it interacts with other web metrics becomes key. As we consider how to boost these interactions, it’s worth examining the broader array of factors that influence search engine rankings.
How to Improve Your Search Engines Ranking Factors
Improving your search engine rankings involves addressing various factors, whether enhancing local search capabilities or speeding up your page load times. Each factor, from core web vitals to outdated links, plays a role in your site’s SEO performance.
While each ranking factor offers distinct advantages, the right optimization approach is essential. Effective SEO isn’t just about making isolated adjustments; it requires a comprehensive strategy considering every potential improvement.
Small changes can have big impacts. Adopting practical measures like focusing on content quality, swiftly addressing site issues, and continually testing new strategies can drive significant improvements.
By employing common sense and maintaining a commitment to high-quality output and prompt problem resolution, you set the stage for sustained enhancements in your site’s search engine visibility.
Use Common Sense
Not all of the SEO ranking factors here are equally important. Optimizing image alt text for Google image search users may be important, but it is nowhere near as important as boosting your horrendously slow page speed.
Prioritize each particular search ranking factor based on how much damage it would do. It is usually quite easy to tell how much of a problem SEO ranking factors are based on common sense alone, so deal with the biggest problems first.
That being said, do not be afraid to tackle the smaller issues if you get time. Low-quality directory links in your link profile might be less urgent than improving your core web vitals, but it never hurts to cull spammy inbound links if you get a chance.
Focus on High-Quality Content
Content is the core of anything you do with SEO. Most of these SEO ranking factors are pointless to pursue without some good content actually backing them up.
Make sure that you always produce good content before you begin to focus on the smaller SEO ranking factors. Having a solid piece of base content is the best way to kickstart your ranking optimization and push it in the right direction.
Creating this content usually means that you have also established search intent and maybe even used specialized tools to browse user search history or the keywords that led them to your site. This information is invaluable for so many different tasks that there is no reason not to gather it.
Resolve Issues Quickly
Whether you have been accidentally keyword-stuffing your blog posts or have too many broken links amongst your inbound links, resolving these issues quickly is the best way to ensure that your site is back to how it should be.
Ranking factors are what determine whether you are on the first page of the results or the four-hundredth. If you notice any issues, make sure you start working on fixing them before they can tank your current rankings.
In most cases, rankings will not update until Google does another crawl of your site. However, not even tools like Google Search Console can tell you when that will happen.
You do not want to fix major issues with your site right after a new crawl has pushed the updated search rankings out, so try to resolve problems as soon as you can.
Keep Experimenting
While SEO professionals know quite a lot about Google’s ranking algorithms, there is not a one-size-fits-all way to tackle them.
In some cases, one site might have a very specific search intent to target. In others, local ranking factors may matter more than country-wide rankings and search results.
A huge part of SEO is finding a niche and claiming it as your own, so do not be afraid to try things that are not necessarily being done by other businesses in your industry.
While you never want to do anything that could risk destroying your entire SEO campaign, taking a few risks here and there can sometimes pay off in unexpected ways.
Concluding Insights: What We’ve Learned About Google Ranking Factors
There are a lot of ranking factors out there, far too many to include in this list.
Many of them have only minor benefits when used on their own, but they can still be a powerful tool to use if you are squeezing as much potential out of your site as possible.
Remember that there is no sure-fire way to guarantee success and that you will need to approach each ranking factor in a way that makes sense for your website and business.